| Population | Group | Sample Size | Ref Allele | Alt Allele |
|---|
The highly complex structure of the human brain is strongly shaped by genetic influences
1. Subcortical brain regions form circuits with cortical areas to coordinate movement
2, learning, memory
3 and motivation
4, and altered circuits can lead to abnormal behaviour and disease
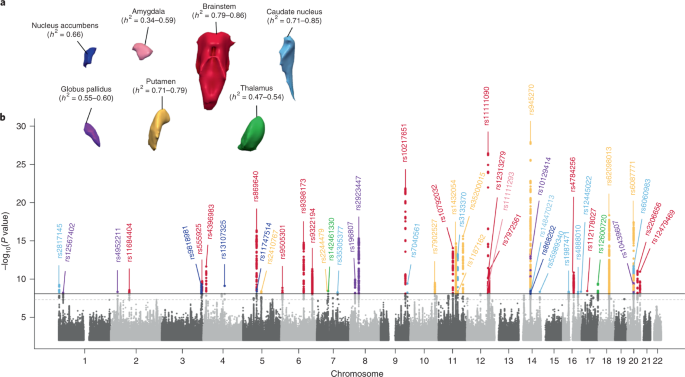
2. To investigate how common genetic variants affect the structure of these brain regions, here we conduct genome-wide association studies of the volumes of seven subcortical regions and the intracranial volume derived from magnetic resonance images of 30,717 individuals from 50 cohorts. We identify five novel genetic variants influencing the volumes of the putamen and caudate nucleus. We also find stronger evidence for three loci with previously established influences on hippocampal volume
5 and intracranial volume
6. These variants show specific volumetric effects on brain structures rather than global effects across structures. The strongest effects were found for the putamen, where a novel intergenic locus with replicable influence on volume (rs945270;
P = 1.08 × 10−33; 0.52% variance explained) showed evidence of altering the expression of the
KTN1 gene in both brain and blood tissue. Variants influencing putamen volume clustered near developmental genes that regulate apoptosis, axon guidance and vesicle transport. Identification of these genetic variants provides insight into the causes of variability inhuman brain development, and may help to determine mechanisms of neuropsychiatric dysfunction.
At the individual level, genetic variations exert lasting influences on brain structures and functions associated with behaviour and predisposition to disease. Within the context of the Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) consortium, we conducted a collaborative large-scale genetic analysis of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to identify genetic variants that influence brain structure. Here, we focus on volumetric measures derived from a measure of head size (intracranial volume, ICV) and seven subcortical brain structures corrected for the ICV (nucleus accumbens, caudate, putamen, pallidum, amygdala, hippocampus and thalamus). To ensure data homogeneity within the ENIGMA consortium, we designed and implemented standardized protocols for image analysis, quality assessment, genetic imputation (to 1000 Genomes references, version 3) and association (
Extended Data Fig. 1 and Methods).